Emotions aren’t just mental—they have real effects on our physical well-being. From digestive discomfort to respiratory strain, our emotional states can influence a wide array of bodily functions. Let’s explore how emotions impact key organs and what you can do to protect your health.
Primary Keyword
“emotions affect organs” (used six times naturally in the article)
Related Keywords
- mind-body connection
- stress hormones
- digestive health
- chronic emotional stress
- gut-brain axis
- emotional well-being
- organ function
- physical health
How Emotions Impact the Body: A Closer Look
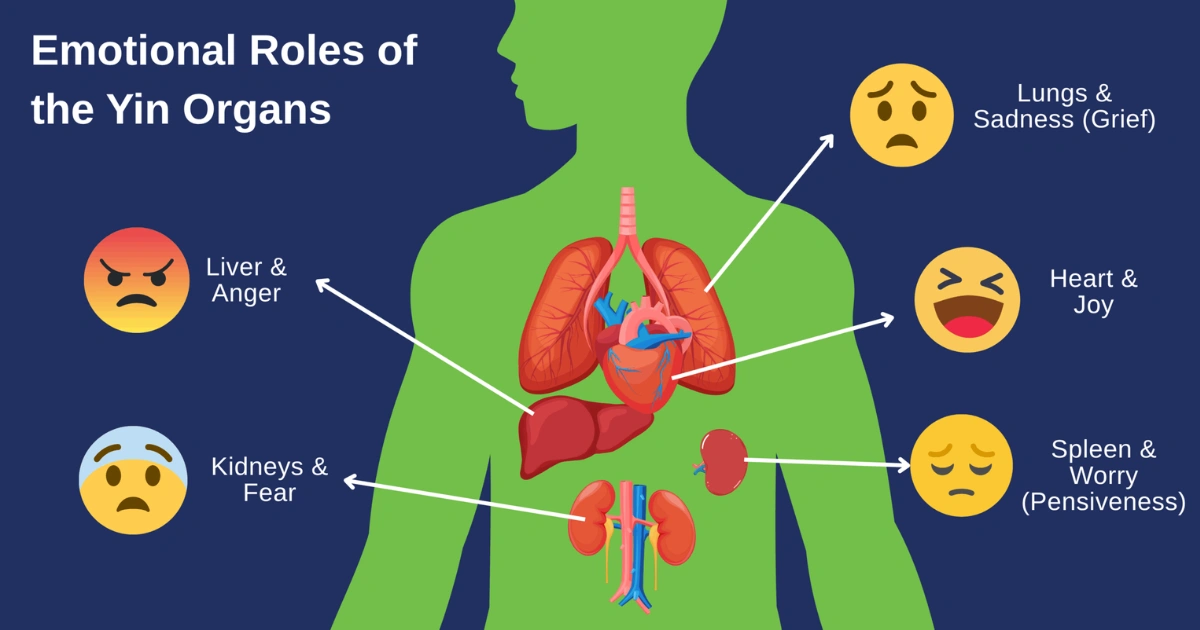
Worry and the Digestive System
Excessive worry or rumination activates the fight-or-flight response, diverting blood away from the digestive tract. This reduces enzyme secretion, slows digestion, and may lead to bloating or indigestion. Studies show chronic anxiety increases risk of acid reflux, irritable bowel syndrome (IBS), ulcers, and gut inflammation.husknaturopathy.com.auEatingWellPMC
Stress and the Gut-Brain Axis
Stress triggers hormone release (like cortisol and adrenaline), which disrupts gut motility, alters microbiota balance, and increases gut permeability (“leaky gut”). This weakens digestion, heightens inflammation, and creates a feedback loop with the nervous system known as the gut‑brain axis.STM JournalsHarvard HealthThe Times of India
Anger and Liver Health
In holistic traditions and emerging biomedical research, chronic anger is linked to increased inflammation and oxidative stress in the liver. Over time, this can contribute to fatty liver disease and impaired metabolic functions.Doctor.ndtv.comeva.thebustednews.com
Fear and Kidney Strain
When fear becomes constant, the resulting hormonal imbalance burdens kidney filtration and energy regulation. This can contribute to fatigue and endocrine disruptions.Doctor.ndtv.comBaltimore Chronicle
Sadness, Grief, and Respiratory Function
Sadness and grief often manifest in the lungs. Long periods of grief may lead to shallow breathing or chest tightness, impairing oxygen intake and reducing lung efficiency.Doctor.ndtv.comeva.thebustednews.comBaltimore Chronicle
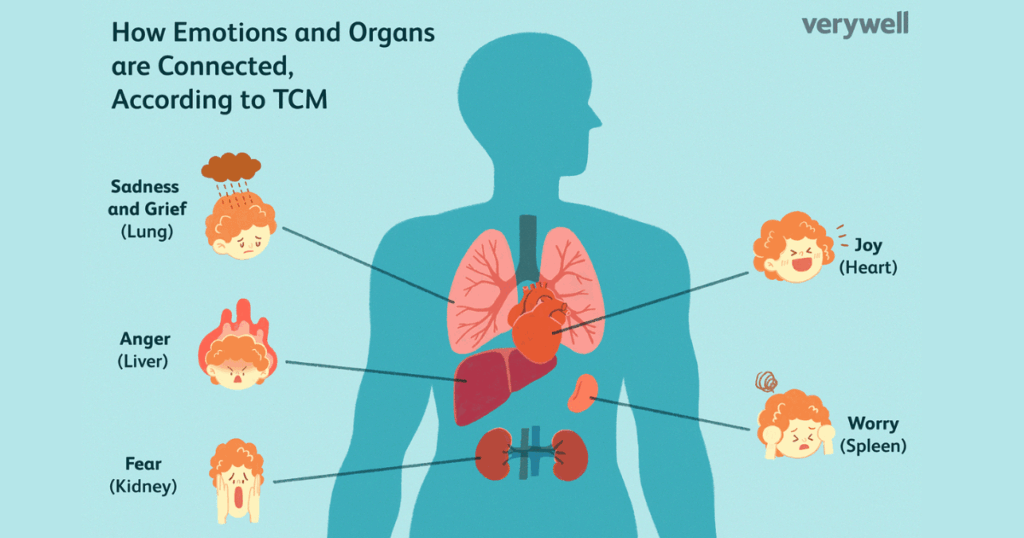
Stress and the Heart & Brain
Chronic stress elevates blood pressure and triggers inflammatory processes in blood vessels. It also impacts the brain by impairing memory and focus through hippocampal shrinkage and neurotransmitter disruption.Doctor.ndtv.comApollo 24|7Samatva | Yoga
How Emotions Affect Organs: At a Glance
| Emotion | Affected Organs | How It Impacts Them |
|---|---|---|
| Worry | Digestive system | Slows digestion, causes IBS, acid reflux, inflammation |
| Stress | Gut, heart, brain | Hinders digestion, raises blood pressure, impairs focus |
| Anger | Liver | Inflammation, fatty liver, reduced detox capabilities |
| Fear | Kidneys | Hormonal imbalance, fatigue, compromised filtration |
| Sadness/Grief | Lungs, heart | Shallow breathing, oxygen limitations, circulation issues |
Practical Ways to Support Organ Health Through Emotional Balance
- Practice stress resilience: Mindfulness, meditation, deep breathing, and regular exercise help lower cortisol and support the parasympathetic (rest-and-digest) state.Apollo 24|7The Times of India
- Prioritize gut care: Maintain gut health through probiotics, hydration, gentle foods, and reduced caffeine or processed items.Apollo 24|7EatingWell
- Release tough emotions: Therapy, journaling, somatic practices (like somatic tracking), or supportive social connection can ease emotional strain and regional tensions.husknaturopathy.com.auReddit
- Support organ resilience: Adequate sleep, balanced nutrition (vitamins C & D), and cardiovascular-friendly habits like walking or yoga protect heart and brain function.Apollo 24|7The Human Project Foundation
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
1. Can emotions really affect organs?
Absolutely. The stress response alters blood flow, hormone balance, and neural signals, all of which can impair organ function over time.
2. How does stress slow digestion?
Stress activates the sympathetic nervous system, reducing blood supply to the gut, inhibiting peristalsis, and lowering enzyme production—leading to bloating, pain, and IBS.Biology InsightsEatingWell
3. Is there a scientific link between emotions and organ conditions like ulcers or fatty liver?
Yes. Mendelian randomization studies indicate anxiety and depression are linked to upper gastrointestinal diseases like ulcers. Additionally, anger-related inflammation may harm liver cells.PMCeva.thebustednews.com
4. What role does the gut-brain axis play in these effects?
The gut and brain communicate via neural and hormonal pathways. Emotional distress can alter gut motility, microbiota, and even immune responses, creating a feedback loop that worsens both emotional and physical symptoms.Harvard HealthSTM Journals
5. What immediate steps help reduce emotional strain on organs?
Engage in deep breathing, physical movement, sleep, balanced nutrition, and emotional processing (e.g., therapy, journaling). Small, consistent actions make a big difference over time.
Suggested Internal Links (secretsofthegreengarden.com)
- Discover Why Mindful Breathing Nourishes Your Gut – Tap into breathing practices that lower stress and support digestion.
- Top 10 Superfoods That Calm Your Emotions Naturally – Explore how nutrient-rich foods can modulate stress responses and improve gut-brain balance.
- Healing the Heart: Emotional Wellness Meets Heart Health – Learn how emotional balance supports cardiovascular strength and resilience.

nserk6
269fpx
49x72o
bb3o75
6t0wkc
Thanks for the marvelous posting! I certainly enjoyed reading it, you could be a great author.I will make sure to bookmark your blog and will often come back sometime soon. I want to encourage that you continue your great writing, have a nice holiday weekend!
Hi , I do believe this is an excellent blog. I stumbled upon it on Yahoo , i will come back once again. Money and freedom is the best way to change, may you be rich and help other people.
t6wgn8
e4kp60
Wow! Thank you! I always wanted to write on my site something like that. Can I include a part of your post to my blog?
svaoaf
ulal84
Loving the info on this web site, you have done outstanding job on the blog posts.
6upsmz
m3lhuw
nuoc7u
Very nice design and fantastic written content, hardly anything else we want : D.
**mind vault**
mind vault is a premium cognitive support formula created for adults 45+. It’s thoughtfully designed to help maintain clear thinking
**mind vault**
mind vault is a premium cognitive support formula created for adults 45+. It’s thoughtfully designed to help maintain clear thinking
**glpro**
glpro is a natural dietary supplement designed to promote balanced blood sugar levels and curb sugar cravings.
**sugarmute**
sugarmute is a science-guided nutritional supplement created to help maintain balanced blood sugar while supporting steady energy and mental clarity.
Thank you for any other wonderful article. Where else may anybody get that kind of info in such a perfect approach of writing? I have a presentation next week, and I’m at the search for such info.
**vittaburn**
vittaburn is a liquid dietary supplement formulated to support healthy weight reduction by increasing metabolic rate, reducing hunger, and promoting fat loss.
**synaptigen**
synaptigen is a next-generation brain support supplement that blends natural nootropics, adaptogens
**glucore**
glucore is a nutritional supplement that is given to patients daily to assist in maintaining healthy blood sugar and metabolic rates.
**prodentim**
prodentim an advanced probiotic formulation designed to support exceptional oral hygiene while fortifying teeth and gums.
**nitric boost**
nitric boost is a dietary formula crafted to enhance vitality and promote overall well-being.
**sleeplean**
sleeplean is a US-trusted, naturally focused nighttime support formula that helps your body burn fat while you rest.
**wildgut**
wildgutis a precision-crafted nutritional blend designed to nurture your dog’s digestive tract.
**mitolyn**
mitolyn a nature-inspired supplement crafted to elevate metabolic activity and support sustainable weight management.
**yusleep**
yusleep is a gentle, nano-enhanced nightly blend designed to help you drift off quickly, stay asleep longer, and wake feeling clear.
**zencortex**
zencortex contains only the natural ingredients that are effective in supporting incredible hearing naturally.
I think this website holds very great indited written content posts.
**breathe**
breathe is a plant-powered tincture crafted to promote lung performance and enhance your breathing quality.
**prostadine**
prostadine is a next-generation prostate support formula designed to help maintain, restore, and enhance optimal male prostate performance.
you have a great blog here! would you like to make some invite posts on my blog?
I am not certain the place you’re getting your information, but great topic. I must spend some time learning much more or working out more. Thanks for wonderful info I used to be looking for this information for my mission.
**pineal xt**
pinealxt is a revolutionary supplement that promotes proper pineal gland function and energy levels to support healthy body function.
**energeia**
energeia is the first and only recipe that targets the root cause of stubborn belly fat and Deadly visceral fat.
**prostabliss**
prostabliss is a carefully developed dietary formula aimed at nurturing prostate vitality and improving urinary comfort.
**boostaro**
boostaro is a specially crafted dietary supplement for men who want to elevate their overall health and vitality.
https://t.me/s/topslotov
**potent stream**
potent stream is engineered to promote prostate well-being by counteracting the residue that can build up from hard-water minerals within the urinary tract.
zlq08o
//t.me/s/official_1win_aviator](https://t.me/s/official_1win_aviator)
**hepato burn**
hepato burn is a premium nutritional formula designed to enhance liver function, boost metabolism, and support natural fat breakdown.
**hepatoburn**
hepatoburn is a potent, plant-based formula created to promote optimal liver performance and naturally stimulate fat-burning mechanisms.
**flow force max**
flow force max delivers a forward-thinking, plant-focused way to support prostate health—while also helping maintain everyday energy, libido, and overall vitality.
**neurogenica**
neurogenica is a dietary supplement formulated to support nerve health and ease discomfort associated with neuropathy.
**cellufend**
cellufend is a natural supplement developed to support balanced blood sugar levels through a blend of botanical extracts and essential nutrients.
**prodentim**
prodentim is a forward-thinking oral wellness blend crafted to nurture and maintain a balanced mouth microbiome.
**revitag**
revitag is a daily skin-support formula created to promote a healthy complexion and visibly diminish the appearance of skin tags.
https://t.me/reiting_top10_casino
https://t.me/s/reiting_top10_casino/9
https://t.me/s/reiting_top10_casino/3
https://t.me/s/reiting_top10_casino
https://t.me/reiting_top10_casino/10
https://t.me/reiting_top10_casino/9
https://t.me/s/reiting_top10_casino/10
https://t.me/s/reiting_top10_casino/5
https://t.me/s/reiting_top10_casino/8
https://t.me/reiting_top10_casino/3
https://t.me/s/reiting_top10_casino/6
https://t.me/reiting_top10_casino/5
https://t.me/s/reiting_top10_casino/2
https://t.me/reiting_top10_casino/6
https://t.me/s/reiting_top10_casino/4
https://t.me/reiting_top10_casino/7
https://t.me/s/Gaming_1xbet
https://t.me/s/PlayCasino_1xbet
https://t.me/s/PlayCasino_1win
https://t.me/s/PlayCasino_1win
https://t.me/s/PlayCasino_1xbet
**memorylift**
memorylift is an innovative dietary formula designed to naturally nurture brain wellness and sharpen cognitive performance.
https://t.me/s/ofitsialniy_1win/33/Reino
https://t.me/s/ofitsialniy_1win
https://t.me/s/iw_1xbet
https://t.me/s/Official_beefcasino
https://t.me/s/bs_1xbet/24
https://t.me/bs_1xbet/16
https://t.me/s/Best_promocode_rus/224
https://t.me/Best_promocode_rus/1111
https://t.me/s/Ud_rIoBet
https://t.me/s/Ud_monRo
https://t.me/s/Ud_FlagMAN
https://t.me/s/tf_1win
https://t.me/s/uD_mArTIN
https://t.me/s/UD_gGbET
https://t.me/s/ud_DRagoNmonEY
https://t.me/s/kef_Lex
https://t.me/s/ke_Volna
https://t.me/s/ke_mellstroy
https://t.me/s/ke_Sol
https://t.me/s/ke_Vulkan
https://t.me/s/ke_DragonMoney
https://t.me/s/kef_beef
https://t.me/s/ke_Monro
https://t.me/s/ke_GGBet
https://t.me/s/ke_1xbet
https://t.me/s/ke_Gama
https://t.me/s/ke_PlayFortuna
https://t.me/s/ke_Pokerdom
https://t.me/s/ke_Drip
https://t.me/s/ke_Flagman
https://t.me/s/ke_Riobet
https://t.me/s/ke_Izzi
https://t.me/s/ke_kent
https://t.me/s/ke_Leon
https://t.me/s/ke_1Win
https://t.me/s/ke_1Go
https://t.me/s/ke_Jet
https://t.me/s/ke_Pinco
https://t.me/s/ke_MrBit
https://t.me/s/ke_Starda
https://t.me/s/ke_Casino_X
https://t.me/s/ke_Fresh
https://t.me/s/ke_Irwin
https://t.me/s/ke_MostBet
https://t.me/s/top_kazino_z
https://t.me/s/topcasino_v_rossii
https://t.me/a_Top_onlinecasino/3
https://t.me/a_Top_onlinecasino/17
https://t.me/topcasino_rus/
https://t.me/s/official_R7_es
https://t.me/s/official_Gizbo_es
https://t.me/s/official_Kent_ed
https://t.me/s/official_Vulkan_es
https://t.me/s/official_Irwin_ed
https://t.me/s/official_Rox_es
https://t.me/s/iGaming_live/4596
Greetings! Very helpful advice on this article! It is the little changes that make the biggest changes. Thanks a lot for sharing!
https://t.me/iGaming_live/4618
https://t.me/va_1xbet/14
https://t.me/s/va_1xbet/17
Some genuinely select posts on this site, saved to fav.
https://t.me/va_1xbet/6
https://t.me/va_1xbet/22
https://t.me/s/ah_1xbet/22
https://t.me/ah_1xbet/3
https://t.me/s/Best_rating_casino
https://t.me/s/reyting_topcazino/14
https://t.me/topcasino_rus/
https://t.me/a_Topcasino/6
https://t.me/a_Topcasino/8
https://t.me/a_Topcasino/4
https://telegra.ph/Top-kazino-11-14-2
https://t.me/kazino_bez_filtrov
https://t.me/da_1xbet/5
https://t.me/da_1xbet/2
https://t.me/da_1xbet/6
https://t.me/da_1xbet/9
Hi, i read your blog occasionally and i own a similar one and i was just wondering if you get a lot of spam feedback? If so how do you reduce it, any plugin or anything you can advise? I get so much lately it’s driving me mad so any assistance is very much appreciated.
https://t.me/top_online_kazino/5
https://t.me/s/top_online_kazino/4
https://t.me/om_1xbet/13
https://t.me/om_1xbet/9
https://t.me/s/om_1xbet/4
https://t.me/om_1xbet/3
Win chess 1 — сыграй прямо сейчас и получи бонус до 5000 рублей за регистрацию! В 1win ты найдёшь тысячи слотов, ставки на спорт с высокими коэффициентами и лайв-ставки в реальном времени, быстрый вывод выигрышей и кэшбэк до 10%, а также фриспины и промокод для увеличения депозита. Минимальный депозит — всего 100 рублей, а круглосуточная поддержка и личный кабинет обеспечивают комфортную игру в любой момент.
1 win рабочее зеркало — быстро входи в любимое онлайн казино и букмекерскую контору! Получай до 1500? бонусов за депозит, радуйся высоким коэффициентам и выгодным лайв-ставкам, зарабатывай с фриспинами и промокодами, выводи выигрыш в считанные минуты и наслаждайся круглосуточным доступом и быстрыми выплатами.
1 вин это мошенники — выбирай честные онлайн казино и ставки на спорт с 1win! Здесь тебя ждут высокие коэффициенты до 95%, фриспіны за регистрацию, мгновенные выплаты и бонусы за депозит до 50%. Регистрация с промокодом и минимальным депозитом — быстро, просто и доступно круглосуточно.
https://telegra.ph/Beef-kazino-11-25
I simply could not go away your web site prior to suggesting that I extremely loved the usual info a person provide on your guests? Is gonna be again often in order to check up on new posts
Woh I love your posts, saved to bookmarks! .
https://t.me/officials_pokerdom/3856
برای دوستانی که به دنبال یک راهکار مطمئن برای وریفای حساب در بروکرهای فارکس هستند، پیشنهاد میکنم خدمات شوپی را بررسی کنند. این مجموعه به صورت تخصصی، وریفای قانونی حساب های فارکس را با مدارکی ارائه میدهد که کاملاً معتبر بوده و به نام خودتان صادر میشود. این روش دائمی است و ریسک بلاک شدن حساب شما را به صفر میرساند. کیفیت و پشتیبانیشان واقعاً عالی است.
https://t.me/Martin_officials
https://t.me/s/Flagman_officials
https://t.me/s/ROX_officials
https://t.me/s/Drip_officials
https://t.me/s/RejtingTopKazino
Very good blog! Do you have any hints for aspiring writers? I’m planning to start my own blog soon but I’m a little lost on everything. Would you advise starting with a free platform like WordPress or go for a paid option? There are so many options out there that I’m totally overwhelmed .. Any suggestions? Thanks a lot!
https://t.me/s/Beefcasino_officials
Hi there, I discovered your site by the use of Google whilst looking for a comparable subject, your site came up, it looks good. I have bookmarked it in my google bookmarks.
As a Newbie, I am continuously browsing online for articles that can be of assistance to me. Thank you
https://t.me/s/Martin_casino_officials
https://t.me/s/Martin_casino_officials
برای یکی از پروژههام نیاز به پاسپورت ترکیه داشتم و گرافیسو بهترین انتخاب بود. تجربه سفارش خیلی راحت بود و پشتیبانی سریع پاسخگو بود. فایل دیجیتال هم رزولوشن بالایی داشت. اگه دنبال یه پاسپورت ترکیه واقعی با طراحی بینقص هستی، این سرویس واقعاً ارزش امتحان داره.
Mit über 80 aufregenden Spielautomaten und 4 dynamischen Tischspielen ist
für jeden Geschmack und jede Fähigkeitsstufe etwas
dabei. Seit über 75 Jahren sind wir ein erstklassiges Ziel für Live-Tischspiele
und modernes Slot-Gaming und bieten eine unvergleichliche Atmosphäre,
die sowohl elegant als auch energiegeladen ist. Mit über 75 Jahren Tradition haben wir die Kunst der Live-Tischspiele und modernen Slot-Spiele perfektioniert
und bieten ein aufregendes Erlebnis wie kein anderes. Aus dem ursprünglichen Interesse an traditionellen Glücksspielen und Poker
entstand ein Startup, das heute ein erfolgreiches Unternehmen im Glücksspiel-Bereich ist.
Der Bahnhof selbst bietet Gäste-Parkplätze an, die speziell
für Casinobesucher vorgesehen sind.
Ohne Online-Präsenz wissen wir, was dir am wichtigsten ist
– große Boni, Freispiele und niedrige Einstiegshürden. Zu unseren Top-Spielen gehören Französisches Roulette,
Amerikanisches Roulette, Blackjack und Texas Hold’em Poker, während unsere
Spielautomaten eine aufregende Auswahl an Optionen bieten. Mit über 75
Jahren Tradition bietet unser Casino eine beeindruckende
Auswahl an Spielen, die Sie stundenlang unterhalten werden. Erleben Sie die
ultimative Spielatmosphäre in der Spielbank Bad Neuenahr, wo reiche Geschichte auf moderne Aufregung trifft.
Egal, ob Sie ein erfahrener Spieler sind oder einfach nur nach einem einzigartigen Unterhaltungserlebnis suchen, die Spielbank Bad Neuenahr ist das ultimative Ziel für einen unvergesslichen Abend.
Unser professionelles Personal wird all Ihren Bedürfnissen gerecht werden und erstklassigen Service in einer klimatisierten Umgebung
bieten, die leicht zugänglich ist.
References:
https://online-spielhallen.de/rant-casino-cashback-so-holst-du-dir-deinen-einsatz-zuruck/
Just about all of what you articulate happens to be supprisingly accurate and it makes me ponder the reason why I hadn’t looked at this with this light before. Your piece truly did turn the light on for me as far as this specific issue goes. Nevertheless at this time there is just one point I am not too comfy with so while I make an effort to reconcile that with the actual central theme of the point, allow me see just what all the rest of your readers have to point out.Very well done.
High-stakes alternatives are a differentiating aspect
in the crowded Australian casino industry, particularly
for the players looking to place stakes on the upper limits.
We recommend opting for platforms that offer the highest limits for the initial deposit, as this
helps to take advantage of the opening bonus promotion. The task of narrowing down a long list of sites to a select few recommended choices is a fundamental process to ensure the most secure and
trustworthy gaming experiences. The Reef Hotel Casino, located in Cairns City, Queensland,
is the sole casino in the region, offering an extensive range
of punting choices, dining establishments, bars, and live entertainment.
They are the unsung heroes who ensure a smooth and
enjoyable gaming experience for every player.
Additionally, reading reviews and testimonials from other players can give you
an idea of the overall customer satisfaction with a particular casino’s support team.
These offers enhance your gaming experience and increase
your chances of winning. Reliable casinos prioritize customer convenience by offering
a wide range of payment options to choose from.
Look for casinos that also offer progressive jackpots, as these can provide life-changing winnings.
However, Aussies can still enjoy playing at offshore crypto casinos.
It’s not just about the bonuses, it’s also about enjoying a shared experience with
friends. These bonuses aren’t just bait; they significantly elevate the player
experience. Welcome bonuses are a fantastic way for new
players to get started. A wide variety of games from different providers
ensures every player finds something they love, whether
you’re into classic slots, live dealer games, or
trying new options. Secondly, we dive into their game selection, favoring sites that offer a diverse array of high-quality games from reputable developers.
References:
https://blackcoin.co/mega-moolah-reviews-gambling-plays-for-big-wins/
While not as big as the site in Halifax, Casino Nova Scotia Sydney boasts an impressive selection of 250+
slots. McPhillips Street Station Casino is the other major casino in Winnipeg.
This location has been a staple of Winnipeg’s entertainment scene
since 1993.
Just like at Parq Vancouver, Encore Rewards are on offer here.
Starlight Casino boasts a stunning collection of more than 935 slots, including classics and new releases.
Located on a 49-acre estate, River Cree casino is the height of luxury.
References:
https://blackcoin.co/winspirit-casino-login-australia-quick-access-to-premium-gaming/
online betting with paypal winnersbet
References:
http://www.konqisakaxgy.shop
paypal casinos for usa players
References:
https://tiroljobs24.at/unternehmen/online-casino-mit-paypal-einzahlung-die-top-casinos-im-vergleich/
بودن در رتبه اول فقط فروش نیست، “اعتبار” و “پرستیژ” برند شماست. مشتری وقتی ببینه شما بالاتر از همه هستید، شما رو به عنوان مرجع اصلی اون صنعت میشناسه. سایتیگو کمک میکنه این تصویر قدرتمند رو در ذهن مخاطب بسازید. برای اینکه نام برندتون مترادف با کیفیت و صدرنشینی بشه، حتماً نگاهی به راهکار تبدیل سایت به برند اول گوگل در سایتیگو بندازید.
بزرگترین ترس کارفرما اینه که “اگه پول دادم و نشد چی؟”. وقتی یک مجموعه مثل ادزنو کلمه “تضمینی” رو کنار خدماتش میاره، یعنی به قدرت تیم و منابعش ایمان صددرصد داره. این ریسک رو از روی دوش شما برمیداره. من کمتر جایی رو دیدم که انقدر محکم پای نتیجه کارش وایسه. اگه دنبال آرامش خیالی هستید، حتماً از خدمات سئو با ضمانت بازگشت وجه و نتیجه استفاده کنید.
https://t.me/s/portable_1WIN
I got what you intend,saved to bookmarks, very decent website .
Thanks for the sensible critique. Me & my neighbor were just preparing to do a little research about this. We got a grab a book from our local library but I think I learned more from this post. I am very glad to see such excellent information being shared freely out there.