This image compares two common thyroid disorders: hyperthyroidism and hypothyroidism. The thyroid gland, located at the front of the neck, plays a crucial role in regulating metabolism, heart rate, body temperature, and energy levels. When it produces too much or too little hormone, noticeable symptoms can appear.
Hyperthyroidism (Overactive Thyroid)
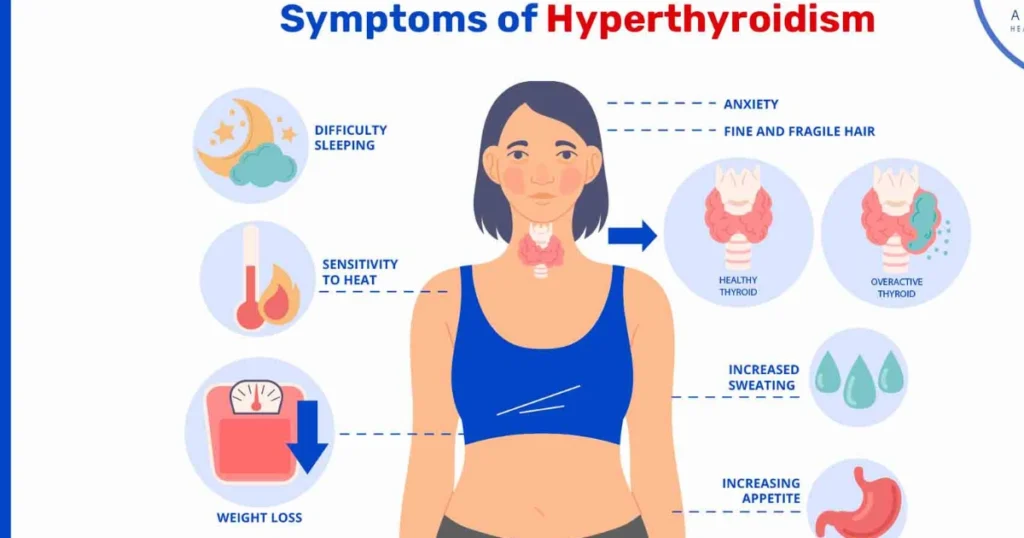
Hyperthyroidism occurs when the thyroid gland produces excess thyroid hormones, causing the body’s systems to speed up.
Common symptoms include:
- Unintentional weight loss
- Heat intolerance
- Tremors or shaking hands
- Restlessness or nervousness
- Rapid or irregular heartbeat
- Enlarged thyroid gland (goiter)
People with hyperthyroidism may feel constantly warm, anxious, and unable to relax, even with adequate rest.
Hypothyroidism (Underactive Thyroid)
Hypothyroidism develops when the thyroid does not produce enough hormones, slowing down many bodily functions.
Common symptoms include:
- Weight gain
- Cold intolerance
- Slow heart rate
- Persistent fatigue
- Dry or rough skin
- Hair thinning or loss
Individuals with hypothyroidism often feel sluggish, cold, and mentally foggy.
Visual Clues Shown in the Image
- The left side illustrates signs of hyperthyroidism, including a more alert facial expression and an enlarged thyroid
- The right side shows hypothyroidism features, such as facial puffiness and signs of slowed metabolism
- The thyroid gland is highlighted in both conditions to show size and activity differences
Why Thyroid Balance Matters
The thyroid affects nearly every organ system. Untreated thyroid disorders can lead to complications involving the heart, metabolism, mental health, and overall quality of life.
Important Note
Symptoms alone are not enough to diagnose thyroid conditions. Blood tests measuring thyroid hormones and medical evaluation by a healthcare professional are necessary for accurate diagnosis and treatment.

