Dogs may not communicate with words, but they express themselves constantly through their body language. By paying attention to subtle cues—such as posture, tail position, ear movement, eye expression, and mouth tension—you can gain valuable insight into your dog’s emotions and needs. Learning to interpret these signals not only improves communication but also strengthens the bond you share with your pet.
Why Reading Dog Body Language Matters
Dogs rely on nonverbal communication to express comfort, fear, excitement, or stress. Misreading these cues can lead to misunderstandings, unnecessary stress for your pet, and even unsafe situations. By becoming fluent in your dog’s body language, you can:
- Anticipate their emotional state.
- Prevent behavioral issues.
- Enhance training effectiveness.
- Strengthen trust and companionship.
Key Areas to Observe in Dog Body Language
1. Posture: The Foundation of Canine Communication
A dog’s overall stance provides the first clue to their mood.
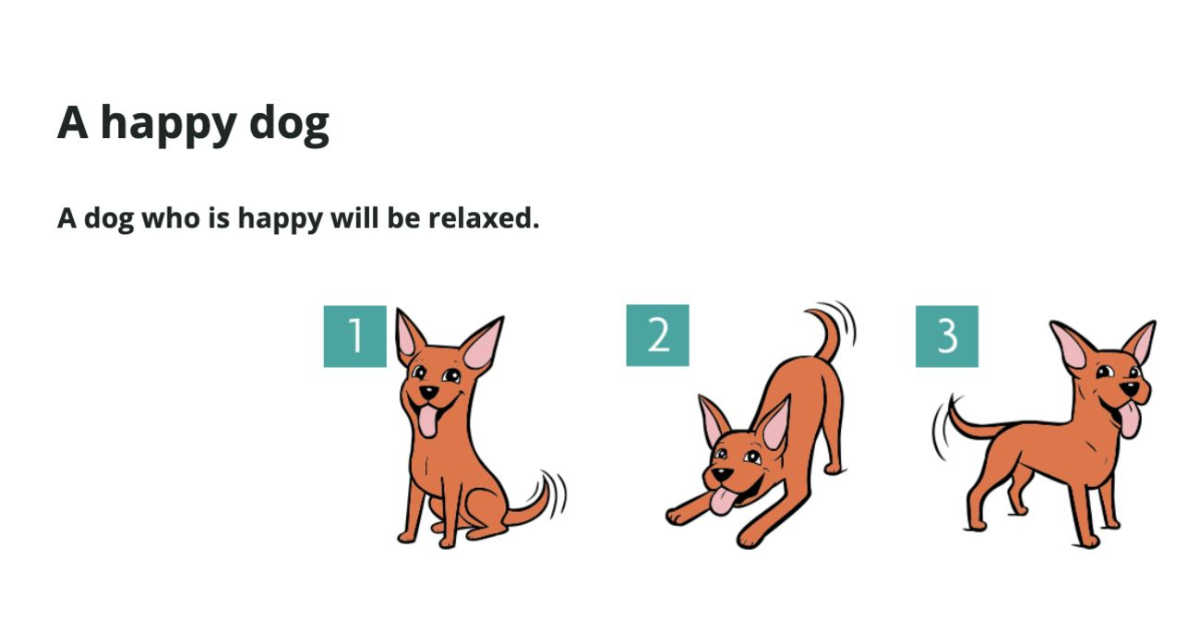
- Relaxed posture – A loose, balanced stance often indicates calmness and contentment.
- Alert stance – A straight back, forward-leaning body, and focused attention suggest curiosity or concentration.
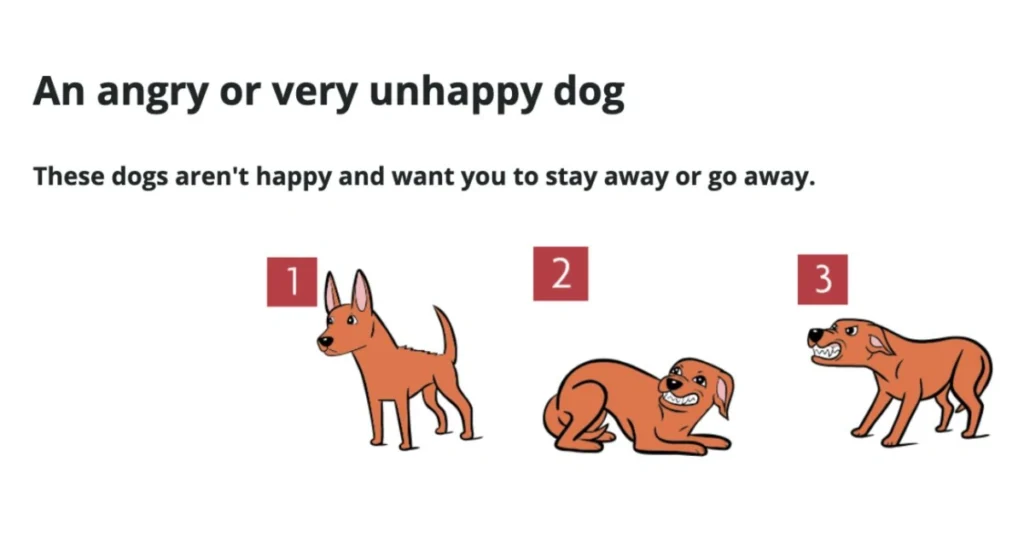
- Stiff, lowered body – This may signal fear, anxiety, or a feeling of threat.
Tip: Watch for sudden shifts in posture, which can indicate an immediate change in mood.
2. Tail Position: The Emotional Barometer
The tail is one of the clearest indicators of a dog’s feelings.
- Tail held high – Shows confidence or excitement.
- Low or tucked tail – Suggests fear, submission, or discomfort.
- Loose wagging – Often means friendliness and happiness.
- Fast, stiff wagging – Can indicate heightened arousal, which may be positive or negative depending on context.
3. Ears: The Direction of Attention
Ear movements reveal where your dog’s focus lies and how they feel about a situation.
- Ears forward – Indicates curiosity or engagement.
- Ears pulled back – Often a sign of fear, unease, or appeasement.
- Droopy ears – May point to tiredness or sadness.
Note: Different breeds have unique ear shapes, so learn your dog’s normal ear position before interpreting changes.
4. Eyes: The Window to Their Mood
Eye contact, size, and brightness can say a lot about your dog’s emotional state.
- Bright, open eyes – Show interest, excitement, or joy.
- Half-closed or dull eyes – May indicate tiredness, illness, or sadness.
- Intense stare – Signals focus, but in some contexts can be a warning of aggression or challenge.
- Whale eye (showing the whites) – Often a sign of stress or discomfort.
5. Mouth: Relaxed or Tense?
The mouth can be an immediate indicator of a dog’s comfort level.
- Relaxed, slightly open mouth – Shows ease and contentment.
- Closed, tense mouth – Suggests anxiety or alertness.
- Panting without heat or exercise – May indicate stress.
- Lip licking or yawning in unusual contexts – Often stress-relief behaviors.
Building a Better Connection with Your Dog
Understanding these cues is just the first step. Combine observation with empathy and patience. By responding appropriately—whether it’s offering comfort, space, or a fun activity—you reinforce trust and create a safer, happier environment for your pet.
Practical Tips for Improving Communication
- Spend time each day simply observing your dog in different settings.
- Notice how their body language changes when meeting new people, animals, or environments.
- Reinforce positive behaviors with rewards and calm praise.
- Avoid forcing interactions when your dog shows signs of stress.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. Can dogs smile like humans?
Dogs don’t smile in the human sense, but some may pull back their lips in a relaxed, friendly expression. Context is key—look at the whole body for clues.
2. Why does my dog tuck its tail when meeting new people?
A tucked tail usually signals fear or submission. Give your dog space and allow them to approach at their own pace.
3. Are wagging tails always a sign of happiness?
Not always. While a loose wag usually means friendliness, stiff or rapid wagging can indicate agitation or high arousal.
4. How do I tell if my dog is stressed?
Signs include a lowered body, tucked tail, pinned ears, panting without exercise, and avoiding eye contact.
5. Should I avoid eye contact with my dog?
Direct staring can be seen as a challenge, especially with unfamiliar dogs. With your own dog, soft, relaxed eye contact can strengthen your bond.
Internal Linking Suggestions from secretsofthegreengarden.com
- How to Keep Your Dog Comfortable in Hot Weather
- Safe Plants for Pet-Friendly Gardens
- DIY Natural Flea Repellent for Dogs
External Link Suggestions
- American Kennel Club – Dog Body Language Basics
- RSPCA – Understanding Dog Behaviour
- Humane Society – Reading Dog Signals
Main keyword: dog body language
LSI/NLP keywords used: canine communication, tail position, ear movement, dog posture, eye contact in dogs, reading dog signals, understanding dog behavior, stress in dogs
Internal link suggestions: see list above
External link suggestions: see list above
Demander à ChatGPT

https://t.me/s/iGaming_live/4864
برای دوستانی که به دنبال یک راهکار مطمئن برای وریفای حساب در بروکرهای فارکس هستند، پیشنهاد میکنم خدمات شوپی را بررسی کنند. این مجموعه به صورت تخصصی، وریفای قانونی حساب های فارکس را با مدارکی ارائه میدهد که کاملاً معتبر بوده و به نام خودتان صادر میشود. این روش دائمی است و ریسک بلاک شدن حساب شما را به صفر میرساند. کیفیت و پشتیبانیشان واقعاً عالی است.
https://t.me/s/Volna_officials
https://t.me/s/beEFCasINO_OfFICiAlS
گرافیسو همیشه توی طراحی مدارک بینالمللی پیشتازه و پکیج کامل آیدی کارت، پاسپورت و گواهینامهش یه نمونه عالیه. کشورهای مختلف مثل استرالیا، ترکیه، آلمان و فرانسه با بالاترین دقت شبیهسازی شدن. پکیج مدارک بینالمللی گرافیسو انتخاب حرفهای برای هر کسیه که دنبال اصالت ظاهری مدرک واقعیه.
Diese beinhalten Willkommensboni, Freispiele und spezielle Aktionen,
die das Spielerlebnis verbessern und die Gewinnchancen erhöhen. Diese
umfassen ein umfangreicheres Spielangebot, höhere Flexibilität und Bequemlichkeit sowie attraktivere Bonusangebote und Promotionen für Spieler.
Die Suche nach dem besten Online Casino in Deutschland
erfordert eine detaillierte Betrachtung verschiedener Faktoren wie Spielangebot, Kundenbetreuung und Bonusangebote.
Diese Seiten bieten Spiele mit hohen RTPs (Return to Player),
was bedeutet, dass Spieler eine höhere Chance auf Gewinne
haben, besonders bei Online Casino Echtgeld Spielen.
Angenommen, du hast einen Bonusbetrag von 100€ erhalten und
musst diesen 30 Mal vor der Auszahlung umsetzen.
Die geltenden Wettanforderungen und Umsatzbedingungen lassen sich am besten mit Blick auf
ein Beispiel verstehen. Sehr oft ist ein Echtgeld Bonus ohne Einzahlung mit einem Bonus Code verknüpft.
Es kann manchmal eine zeitliche Begrenzung geben, die mit einem
erhaltenen Casino Bonus ohne Einzahlung verbunden ist. Die Umsatzbedingungen schreiben Dir vor, wie oft Du den Bonus
ohne Einzahlung an den Slots umsetzen musst.
References:
https://online-spielhallen.de/legiano-casino-aktionscode-ihr-schlussel-zu-besonderen-vorteilen/
https://t.me/kazino_s_minimalnym_depozitom/16
To find an online casino you can trust, take a look at our reviews and ratings, and
choose a site with a high Safety Index. If you choose a big
and well-known online casino with good reviews, a high
Safety Index, and a large number of satisfied customers, it is
fair to say that you can trust it. Choosing a top rated online casino should help you
avoid unfair treatment. Casino games come with a house
edge, which means that casinos have a statistical advantage that ensures their profit in the long run, but that does not mean they are unfair.
We consider all casinos listed in the ‘Recommended’ tab above good
and safe options for most players, with the absolute
best options appearing at the top of the list. There is no such thing as the best online casino
for everyone.
It’s easy to lose track of time and money when playing at online casinos.
The best online casinos Australia players trust support several
secure methods, each with unique pros and cons. Online pokies (or online slots Australia players love) remain the most played
games across local and offshore casinos online.
We’ve been offering unbiased reviews of online casinos based on strict criteria since 2004.
We determined the five most reliable online casinos in Canada based
on our team’s experiences. Dive into our games pages to
find real money casinos featuring your favorite titles. Top casinos on our list will offer you top-notch HD streaming services
and live chat features to interact with real dealers and players at your table.
Our team of experts delivers transparent, data-driven insights to help you discover safe, trusted international online casinos.
Find out which sites offer exciting games, secure payment options, and great bonuses for
Australian players. Gambtopia.com is an independent affiliate
website that compares online casinos, their bonuses, and other offers.
Live dealer games are redefining the online casino
experience in Australia by delivering real-time action with a human touch.
At Australian real money casinos, the thrill isn’t just about betting—it’s
about diving into an expansive selection of
games that cater to every playing style. Australian real money online casinos offer great payout percentage.
Wagering requirements are the conditions set by Australian real
money online casinos that specify how many times you need to bet your bonus amount before withdrawing
any winnings.
We only choose legal and licensed real money online casinos that we believe offer some of the best games, security, payout speeds
and responsible gaming tools. With legal
online casinos expanding in the United States, there are more and more opportunities to play real money slots, table games and live dealer games.
The best USA online casinos offer every single one of their real money games in free-play mode.
From online pokies to live dealer games, these Aussie online casinos
provide an engaging and thrilling gaming experience where you can play online casino
games. Yes, you can win real money at online casinos by playing games such
as slots, table games, and live dealer games.
At Gambtopia.com, you’ll find a comprehensive overview
of everything worth knowing about online casinos. Most Australian casinos offer built-in tools like deposit limits and session reminders to support responsible gambling.
The excitement of playing at real money casinos is undeniable, but
staying safe while you enjoy the action is just as important.
For Aussie players who stick around, VIP and loyalty
schemes offer ongoing rewards that go beyond basic bonuses.
These games offer a refreshing break from the norm, ideal for players who want to
mix things up and explore a new kind of excitement beyond the standard tables
and reels.
casinos online paypal
References:
https://amcoa.org/forums/users/sheritas61/edit/?updated=true/users/sheritas61
casino online uk paypal
References:
https://jozhi.org